AgriTech - Technology and the Future of Food
Technology is set to significantly impact the agriculture industry and transform the way we produce, manage, and distribute food.
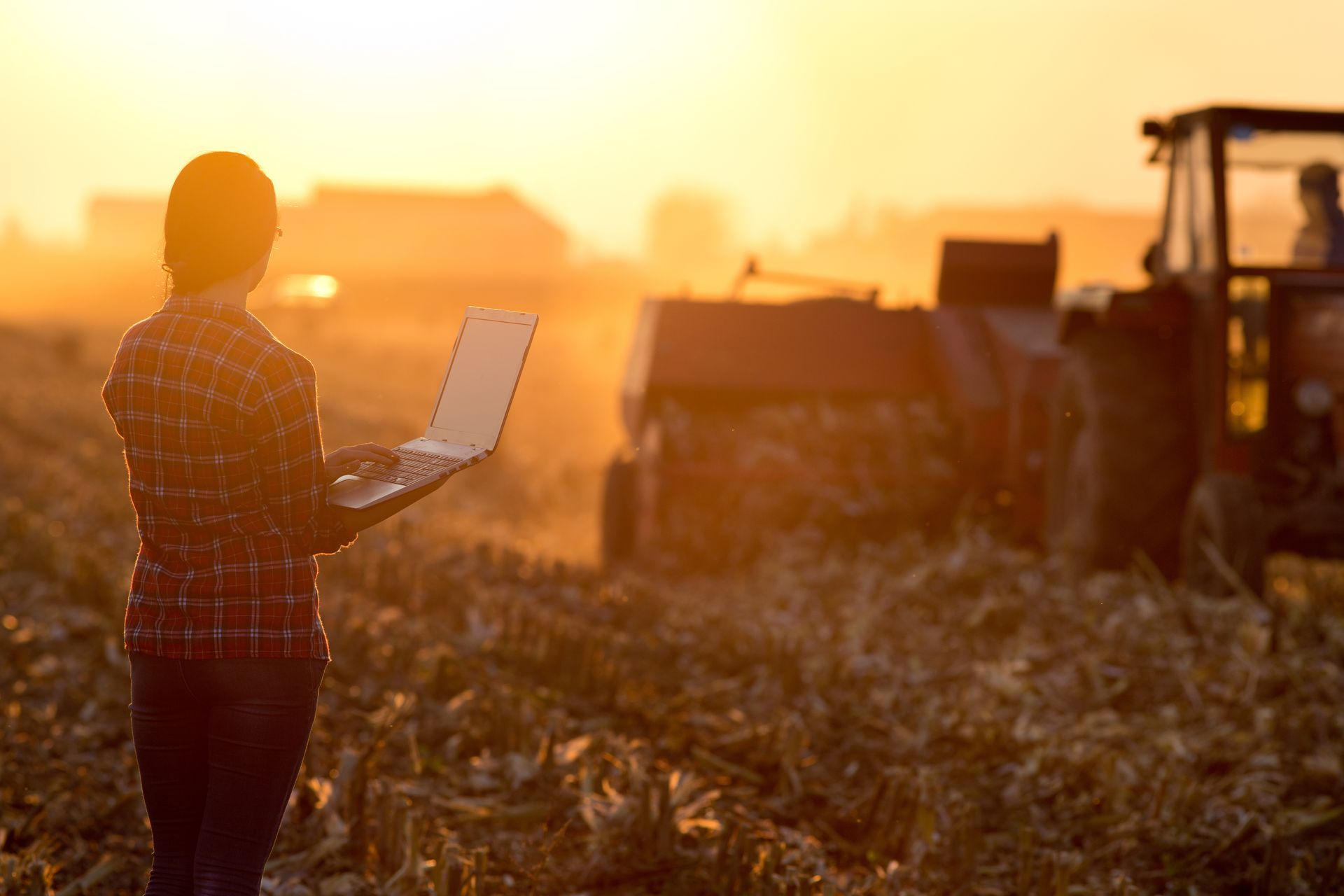

Technology is set to revolutionise food production.
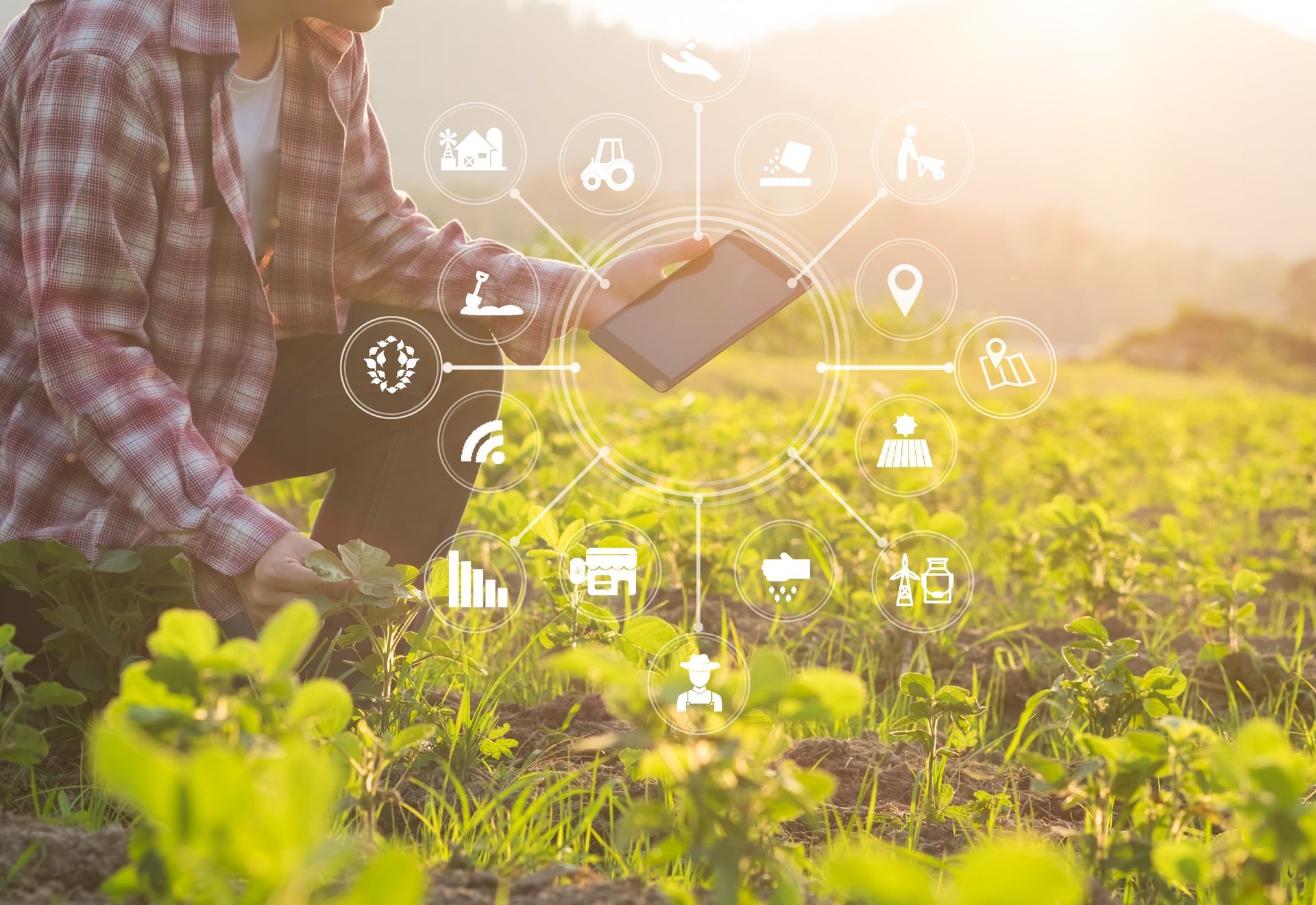
From precision agriculture and robotics to vertical farming and biotechnology, advances in technology are helping farmers increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve sustainability.
These advancements are also enabling new forms of agriculture, such as urban and indoor farming, and making it possible to produce food in areas where traditional farming practices may not be feasible.
As the global population continues to grow, the use of technology in agriculture will become increasingly important in meeting the growing demand for food while also addressing environmental concerns.
Developments in this area include:
- Precision Agriculture: Technology such as GPS mapping, drones, and sensors can be used to optimize planting, irrigation, and fertilizer application, resulting in more efficient and environmentally sustainable farming practices.
- Robotics and Automation: Autonomous machinery can be used for planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency.
- Vertical Farming: Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in a controlled environment, using artificial lighting and temperature regulation. This can increase crop yields, reduce water usage, and eliminate the need for pesticides.
- Biotechnology and Genetics: Advances in biotechnology and genetics can lead to the development of crops that are more resilient to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors, resulting in more productive and sustainable farming practices.
- Blockchain and Traceability: Blockchain technology can be used to track and trace the origin of food products, ensuring greater transparency and accountability in the food supply chain.
The future of technology and agriculture is likely to be characterized by increased efficiency, sustainability, and productivity, as well as greater transparency and traceability in the food supply chain.